With the advent of the Industrial 4.0 era, while enterprises are pursuing efficient production, their requirements for safety management are also constantly increasing. As a key safety technology, lock control has become an important means to ensure industrial production safety and improve production efficiency. In this article, Shengjiu will explore the technical advantages of lock control in depth to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding.
What is the Lock Control?
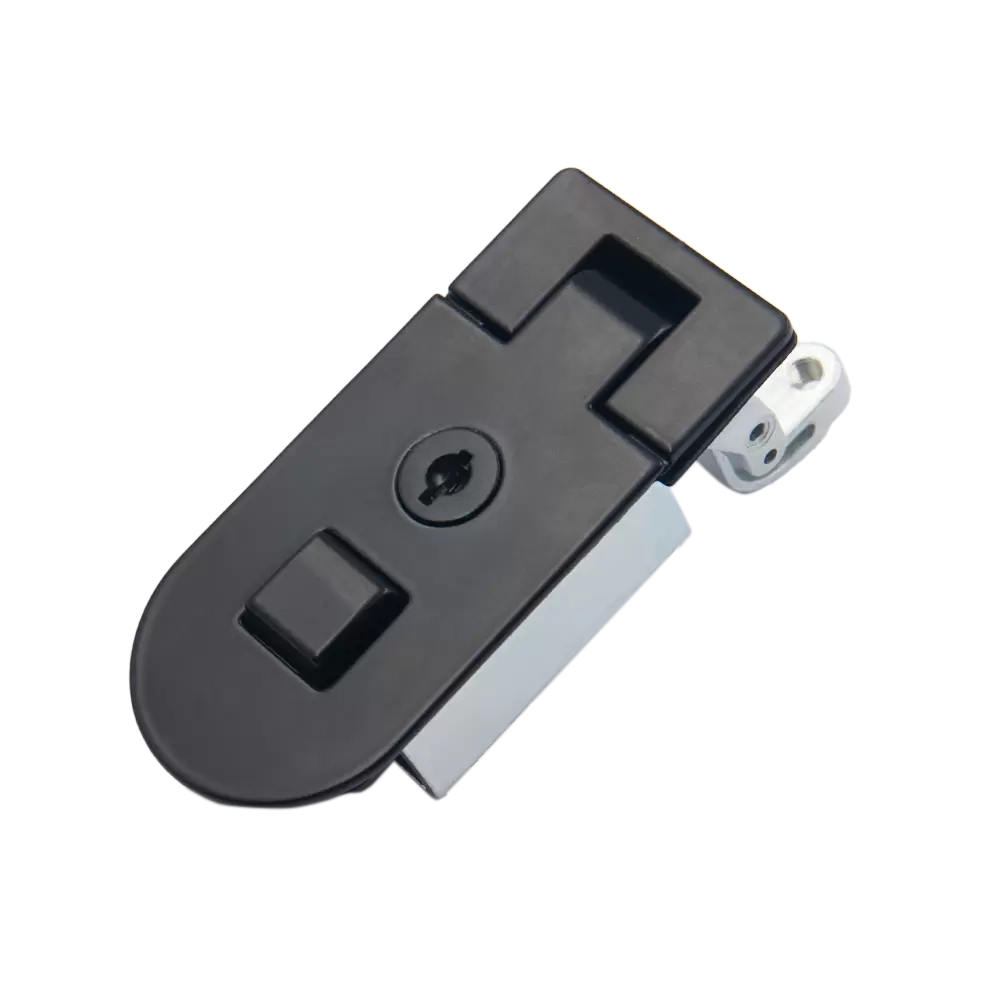

Lock control refers to the management and monitoring of key equipment, processes and operations in industrial production through the use of various locking and control devices to ensure safety and improve efficiency. This system usually includes components such as locks, controllers, sensors, and alarms, which can prevent accidents and illegal operations through mutual cooperation.
The core of lock control is to effectively manage and control the risks that may occur in the production process. In traditional industrial environments, safety accidents occur from time to time, such as equipment misoperation, electrical failures, or chemical leaks. These accidents will not only cause economic losses to the company, but may also pose a serious threat to the personal safety of employees. By introducing a lock control system, companies can effectively reduce safety accidents caused by equipment misoperation or equipment failure, thereby reducing risks and ensuring production safety.
At the same time, with the advancement of technology, the functions of the lock control system are becoming more and more powerful. Not only is it a simple device lock, it can also provide real-time status monitoring and data feedback, allowing managers to find problems faster and take corresponding measures. This ability of real-time monitoring and data analysis makes lock control play an increasingly important role in modern industry.
Technical Advantages of Lock Control in the Industrial Field
1. Improve Equipment Security
In industrial environments, the security of equipment and materials is critical, especially when high-value, sensitive or dangerous items are involved. Lock control can effectively prevent unauthorized personnel from accessing or operating the items in the cabinet by providing strong physical protection. For example, in petrochemical plants, cabinets storing toxic, flammable or explosive substances must be equipped with high-security locks to prevent potential security threats. Lock control usually adopts multi-layer protection mechanisms, such as a combination of mechanical and electronic locks, as well as anti-pry, anti-drill, and explosion-proof designs to ensure that it remains strong and durable when subjected to external attacks or attempted destruction. This high-security design not only prevents the loss and damage of items, but also avoids major safety accidents caused by illegal operations, protecting employee safety and the stability of the production environment.
2. Simplify Management and Control
In industrial facilities, managing multiple lockers and the allocation of permissions is often a complex task. Lock control greatly simplifies this process through digital and automated management functions. Modern lock control usually supports electronic control systems to achieve precise control of cabinets through authentication methods such as password entry, fingerprint scanning, RFID cards or biometric technology. Managers can easily set or change permissions through the centralized management platform, monitor the use of cabinets in real time, and even perform remote operations. In this way, not only the burden of key management is reduced, the security risks caused by key loss or duplication are avoided, but also the time and identity of each operation can be tracked, which is helpful for auditing and responsibility tracing. For example, in pharmaceutical factories, storage cabinets for certain valuable drugs need to strictly control access rights to ensure that only authorized personnel can access drugs to avoid abuse or illegal circulation.
3. Enhance Operational Convenience
With the improvement of industrial automation, operational convenience has become an important factor in improving work efficiency. Although traditional mechanical locks are sturdy, they are inconvenient to operate, especially when a large number of locks need to be managed, and finding and carrying multiple keys may waste a lot of time and energy. Modern lock control integrates intelligent technology to greatly improve operational convenience. For example, when using electronic cabinet locks, operators only need to enter a password, swipe a card, or use fingerprint recognition to quickly unlock the cabinet door. This quick unlocking method is particularly useful in emergency situations, such as when protective equipment or emergency supplies are urgently needed, which can greatly shorten the response time. In addition, some advanced lock controls also support automatic door opening and closing functions. Combined with the factory's automation system, the door will automatically unlock when a person approaches and automatically lock when the person leaves, further simplifying the operation process and reducing the possibility of human operation errors.
4. Improve Durability and Environmental Adaptability
Industrial environments are often very harsh, and there may be extreme temperatures, humidity, dust, chemicals, etc., so the durability and environmental adaptability of lock controls are particularly important. High-quality lock controls usually use high-strength materials such as stainless steel, galvanized steel or special plastics, which can resist corrosion, oxidation and wear, ensuring long-term use in harsh environments without failure. For example, on offshore oil platforms, locks need to withstand the erosion of salt spray and seawater, and at the same time withstand high-intensity mechanical shocks. This design ensures the long life and reliability of the locks, reducing equipment downtime or production interruptions caused by lock damage. In addition, lock controls usually have good sealing to prevent dust, dirt or moisture from entering the lock and keep the lock functioning properly, which is particularly important for industries such as mining and chemicals.
5. Support Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) integration
The rise of Industry 4.0 has promoted the development of smart manufacturing, and the design of lock control has gradually incorporated the concept of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Modern smart cabinet locks can be seamlessly integrated with the factory's management system through the network to achieve remote monitoring and data analysis. For example, through the IIoT platform, managers can monitor the status of all cabinets in real time, including which cabinet is opened, the opening time, the operator and other information. This real-time data acquisition and analysis not only improves the transparency of management, but can also be used to optimize the factory's operating processes. For example, analyzing the frequency and time of cabinet use can help optimize the storage location of items, reduce employee access time, and improve production efficiency. In addition, smart cabinet locks also support alarm functions. When abnormal operations are detected (such as illegal opening or multiple incorrect password inputs), the system can immediately notify the manager and automatically lock the cabinet, further improving security.
6. Prevent Operational Errors and Management Loopholes
In industrial environments, operational errors and management loopholes can have serious consequences, especially in high-risk industries or places that strictly comply with safety regulations. Lock control effectively reduces the occurrence of human errors and management loopholes through precise permission control and detailed operation records. For example, in nuclear power plants or chemical laboratories, the storage of certain operating equipment and materials needs to be strictly controlled, and any unauthorized access may bring significant risks. Lock control can ensure that only specifically authorized personnel can access the items in the cabinet according to the permission settings, and record all details during the operation, including access time, operator identity and specific operation content. These records can help managers quickly find the cause when problems arise and trace responsibility. In addition, by regularly checking and auditing operation records, managers can identify and fix potential management loopholes and ensure that safety regulations are strictly implemented.
These rich technical advantages have made lock control increasingly widely used in modern industry, which not only improves security and management efficiency, but also adapts to the needs of the industrial Internet of Things era, creating a safer and more efficient production environment for enterprises.
With the advent of the Industrial 4.0 era, lock control plays a vital role in modern industry. It not only improves the security of equipment and items, simplifies management processes, enhances the convenience of operation, but also has excellent durability and environmental adaptability. More importantly, the intelligent and IIoT integrated functions of lock control provide enterprises with real-time monitoring, data analysis and remote management capabilities, greatly improving production efficiency and management transparency.
By introducing these advanced lock controls, companies can ensure that safety management is not neglected while pursuing efficient production, thus laying a solid foundation for creating a safer and more efficient production environment. In the future, with the continuous development of technology, lock control will play a more important role in more fields, helping companies meet the opportunities and challenges brought by Industry 4.0.